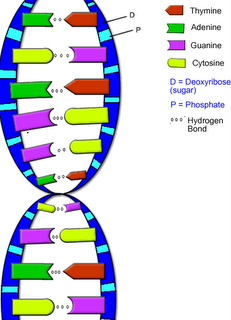
 DNA
DNAYou need to know the structure of DNA. Questions may ask you to label a diagram or name the parts of DNA.
You may have to work out the percentage of one base given the percentage of other bases.
DNA Relpication.The semi-conservative method.
You will have to recall the name of the enzyme involved.
PCR
Task: compare and contrast DNA relpication and PCR
Protein SynthesisRead and learn the steps involved in protein synthesis
Common questions involve you working out the amino acid sequence given either the DNA sense (or nonsense) strand or the mRNA sequence.
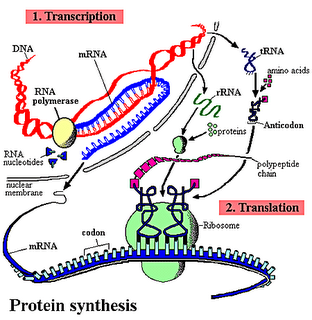 A/S GuruDNA and RNA structureProtein Synthesis
A/S GuruDNA and RNA structureProtein Synthesis
Protein Synthesis (this site is very good for module 1 too)Applications of gene technologyIn recent years we have progressed from the study of genes and genetics to taking a more active role. We now have the ability to identify genes and find out what they do. We can also cut them out and insert them into other organsims, forming
Transgenic organisms.There are two essential types of enzymes used in genetic engineering:
- restriction endonucleases which cut DNA at precise points called recognition sites. Many of these enzymes produce staggered cuts known as sticky ends.
- DNA ligases that stick DNA together.
Genetically engineering
For example: genetically modifying bacteria to make a valuable product e.g. Insulin
Gene therapy
The example you have to know about is for the tratment of cystic fibrosis.
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disease in which the sufferer's lungs get clogged up with a sticky mucus that makes breathing less efficient and cause sufferer's to have many lung infections. CF is inherited when both parents have a faulty allele that codes for a protein called CFTR. In CF the CFTR protein differs in just one of its 1480 amino acids as a result of substitution. This causes the protein not to work. What it should do is pass ions across cell membranes, causing water to follow, hence the mucus is watery. The faulty protein can't, so the resulting mucus is thick and sticky!
Gene therapy is used to replace faulty genes with healthy ones.
The treatment is
temporary and involves:
- Isolation of the healthy CFTR gene, use PCR to clone it.
- Encapsulate the gene into a vector that will carry it into a human lung cell e.g. a liposome (spheres of phospholipids) or a harmless virus.
- Inhale the vector in an aerosol spray.
- The epithelial cells take in the healthy gene, incorporaring it into their DNA and express the gene to make the healthy protein.
- Symptoms are alleviated, but is not permanent.
Life cycles : Mitosis and Meiosis
The diploid number of chromosomes for a species is often described as 2n, e.g. For humans the diploid number is 46. All somatic cells will contain the diploid number. They have this because during mitosis the chromosomes are relpicated - Interphase.
Sex cells or gametes are made through a different type of cell division called meiosis. This reduces the diplod number, 2n, to the haploid number, n, in gametes. Each gamete produced by meiosis gets chromosomes from each homologous pair. When the gametes fuse in fertilisation the zygote will have the diplod number.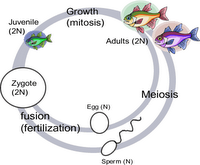
So when answering questions where you have to fill in the chromosome number in a life cycle of an organism, remember to halve the number of chromosomes a cell contains after meiosis e.g in the gametes (sperm and ova) and to use the full number of chromososmes after fertiliasation has taken place. Don't panic if thequestion is about an organism that has adults which may have haploid adults like the water flea!






